Injection molding is a manufacturing process for producing parts by injecting molten material into a mold. Injection molding can be performed with a wide range of plastic materials, including pp, ppr, pe, pet, pvc, pa, and, most commonly, thermoplastic pellets. Material for the part is fed into a heated barrel, mixed, melted, and forced into a mold cavity where it cools and hardens to the configuration of the cavity. The six main step by step process of injection moulding are:
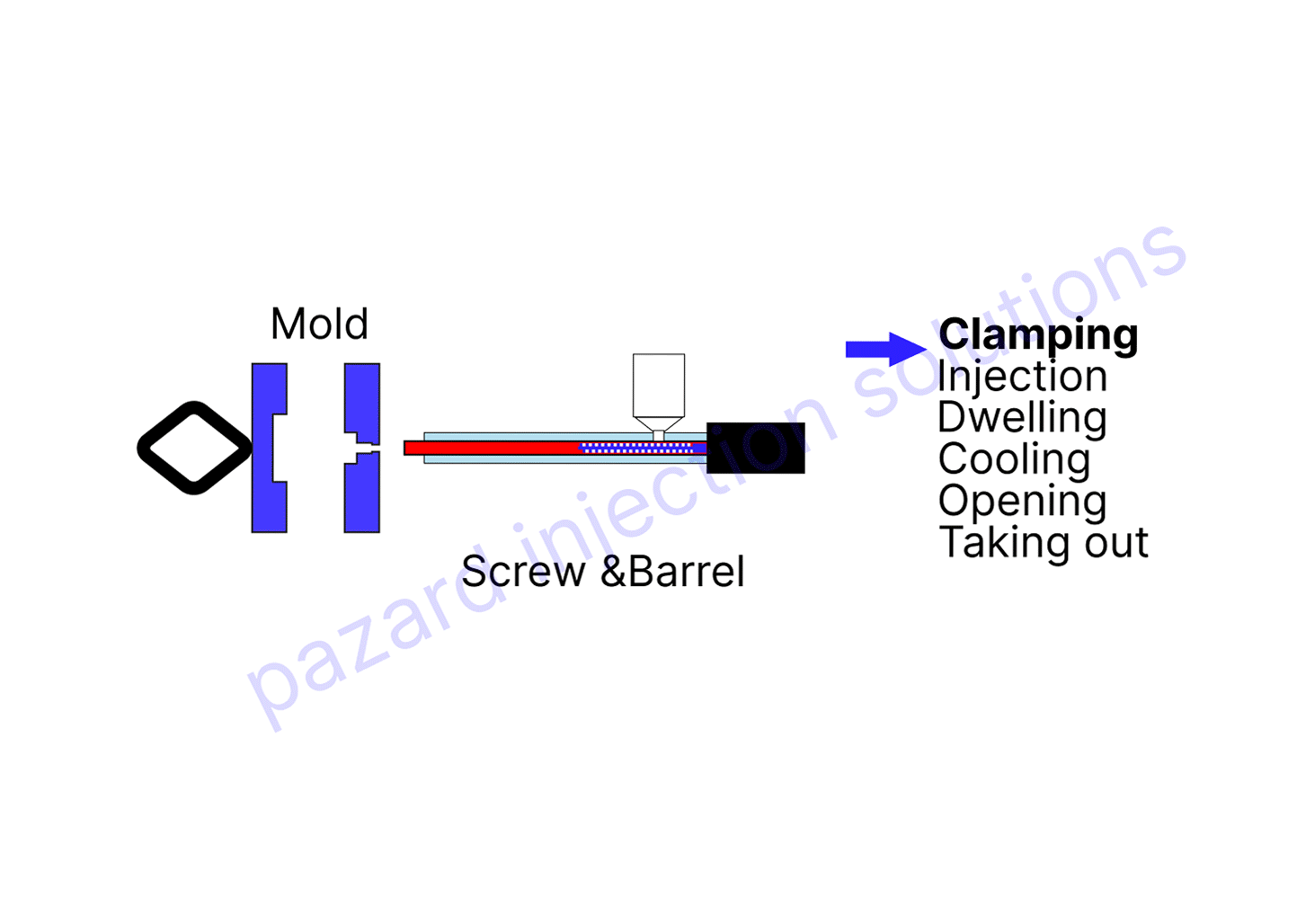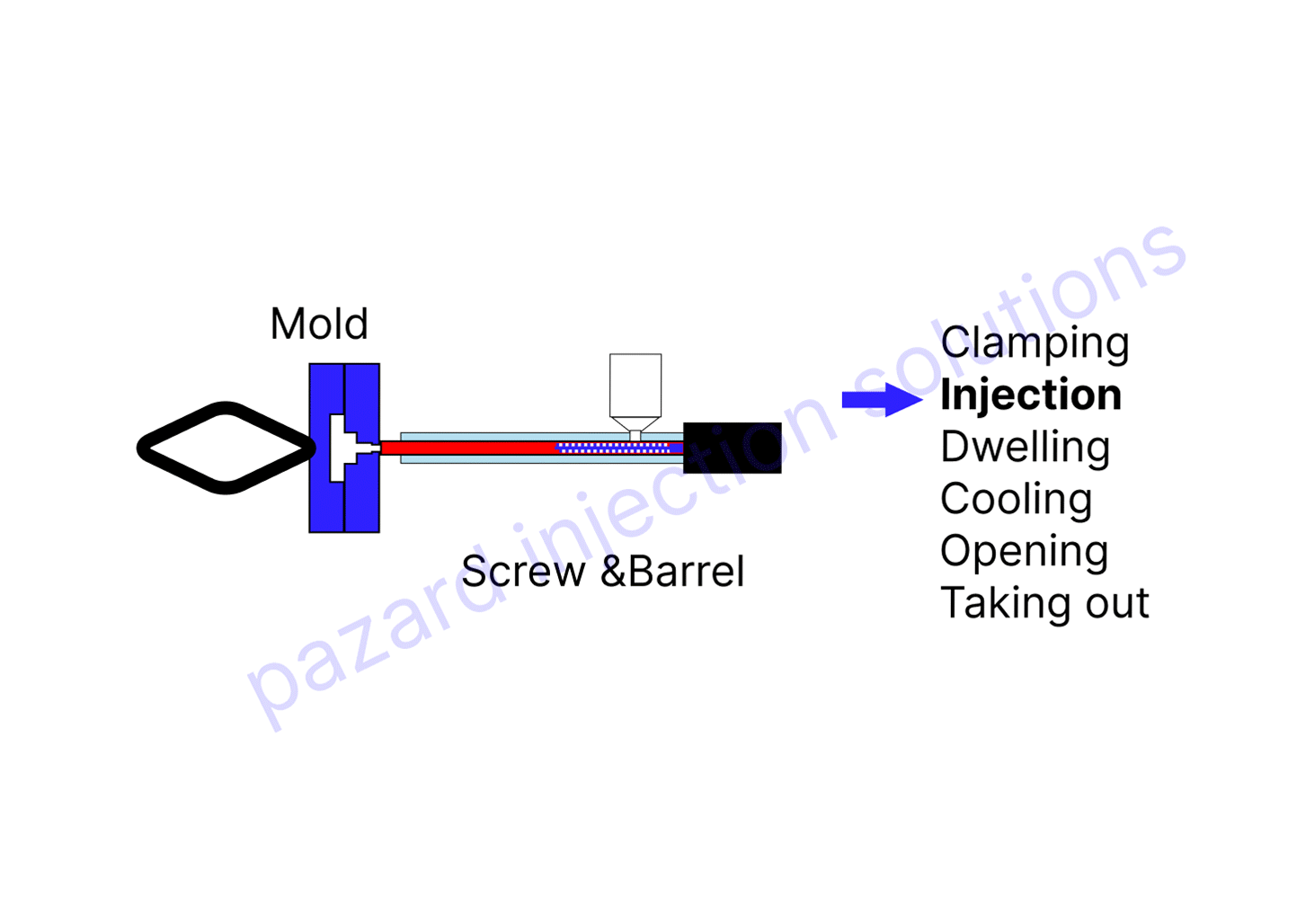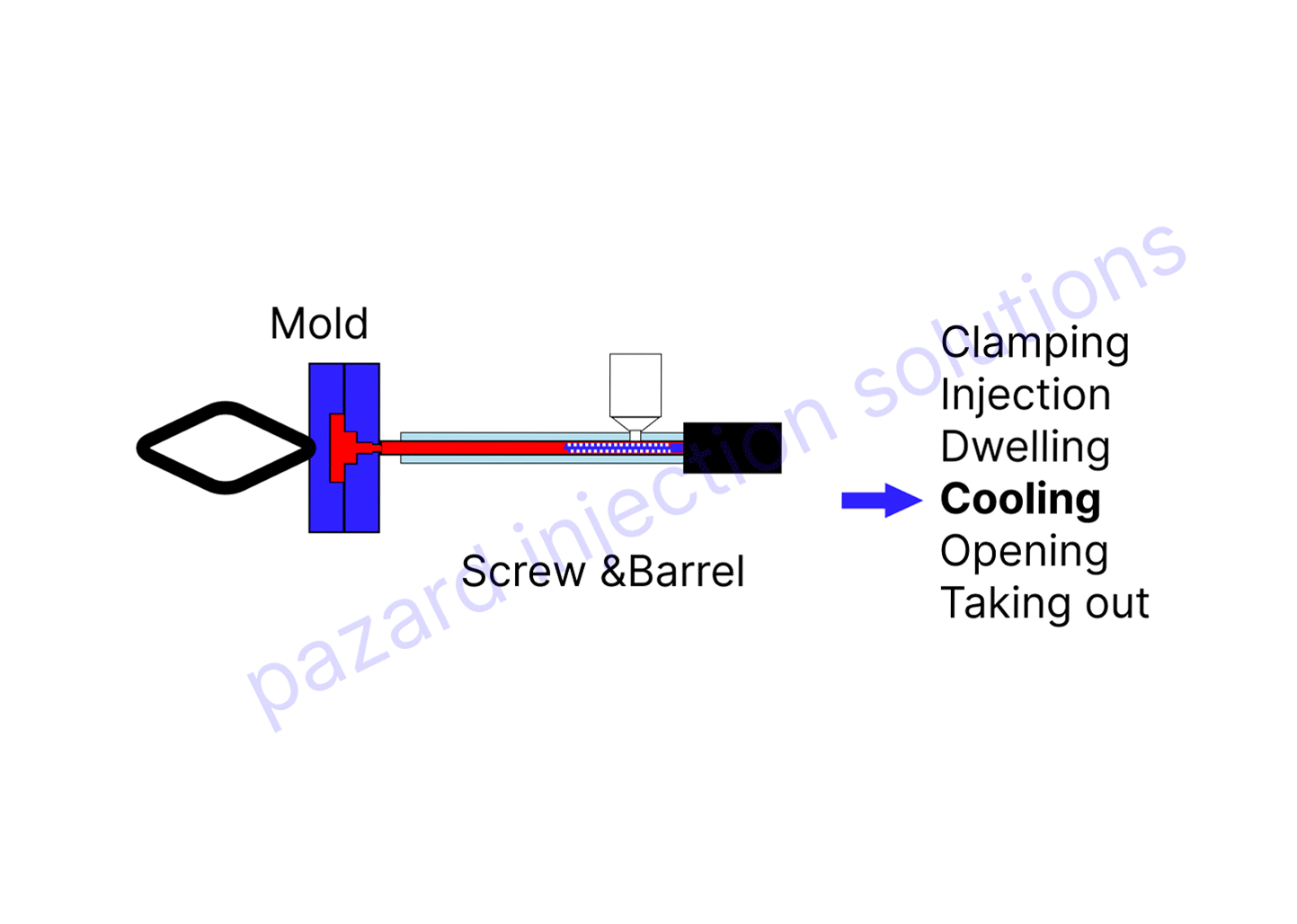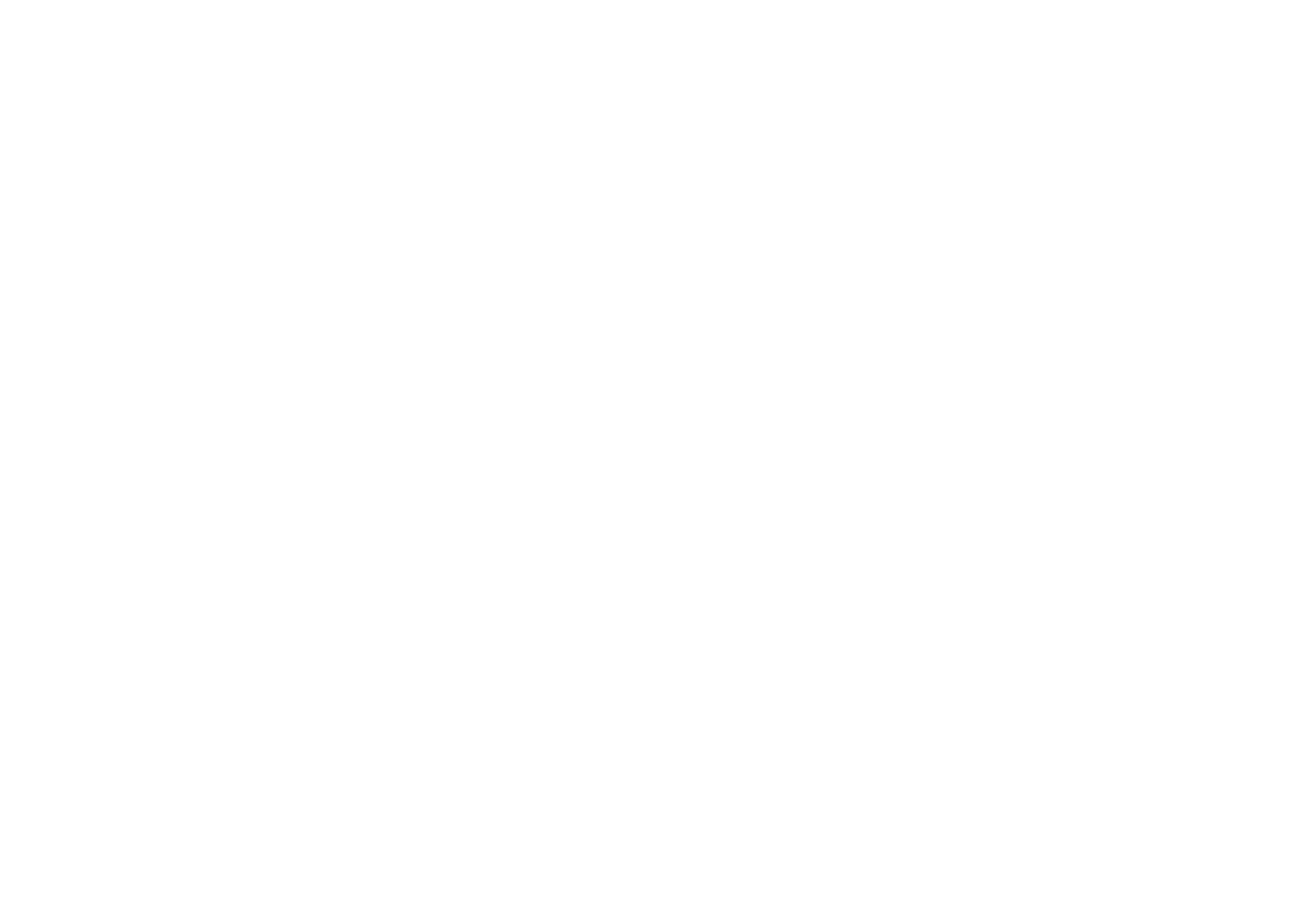
1. Clamping the mold
2. Injecting the material
3. Dwelling
4. Cooling
5. Opening molds
6. Ejecting products out
Clamping the mold
The first step in the injection molding process is to clamp the mold. This is done by closing the two halves of the mold together using a clamping force. The clamping force is necessary to keep the mold from opening during the injection process.
Injecting the material
Once the mold is clamped, the next step is to inject the material into the mold cavity. This is done by injecting the material under high pressure into the mold cavity. The material is injected through a nozzle at the end of the barrel.
Dwelling
After the material is injected into the mold pit, it will begin to cool and solidify. This process is known as a dwelling. During this time, the material will contract, and the mold will start to fill with the material.
Cooling
After the material has solidified, the next step is to cool the mold. This is done by circulating cool water through the mold. The cool water will help to cool the material and prevent it from warping.
Opening the mold
Once the mold is cooled, the next step is to open the mold. This is done by opening the clamping force and separating the two halves of the mold.
Ejecting the product
After the mold is opened, the final step is to eject the product from the mold. This is done by removing the product from the mold cavity. The product is then typically sent to a post-processing station for further finishing.

